When it comes to taking care of your immune health and body’s ability to function properly, there are few nutrients as vital to your system as vitamin D is. Many people are unaware of their vitamin D levels at baseline, let alone if the levels are deficient. So how can you tell if you are vitamin D deficient? What causes vitamin D levels to drop? What are the symptoms and consequences of a vitamin D deficiency? We’re here with the answers.
How to Know if I’m Vitamin D Deficient
The only way to truly understand what your vitamin D levels are, and if you are vitamin D deficient, is by taking a blood test. d.velop™’s convenient at home vitamin D test kit lets you check your vitamin D levels in the comfort of your own home.
What Causes Vitamin D to Drop
There are many reasons for low vitamin D levels. Where you live, the time of year, time spent outside, sun protection, the foods you eat, and certain health conditions all play a role in vitamin D levels. To better understand your situation, the first things you want to think about are your daily activities and habits such as diet or supplementation.
From the food perspective, we start off at a bit of a disadvantage. Vitamin D does not occur naturally in very many foods aside from fatty fish, egg yolks, cod liver oil and fortified food products such as nut/soy milks, orange juice and breakfast cereals. However, it is still difficult to get a lot of vitamin D from what you eat, especially if you are lactose intolerant or vegan.
In terms of activities and tendencies, our time and habits outside also impact our ability to get enough vitamin D. When you spend time outdoors, your body takes the sunlight that hits your skin, and the cholesterol in your skin cells interacts with the UV rays to then break it down into cholecalciferol that your body can use. However, excessive use of sunscreen, and those with darker skin tones tend to have a more difficult time raising their vitamin D levels by spending time in the sun. This is because their skin tends to absorb less UV rays overall. Coupled with more time spent indoors through work or school, vitamin D deficiency is definitely something to consider.
What are the Symptoms of Low Vitamin D
Vitamin D deficiency does not always present with obvious symptoms. However, if you’re worried about potentially being vitamin D deficient, there are a few symptoms you can look for.
Some of the most common indicators of low vitamin D include muscle weakness, bone or joint pain, and fatigue. While a vitamin D deficiency may not start out particularly serious, if left unchecked over time, a vitamin d deficiency can become very dangerous. Chronically low vitamin D levels may lead to loss of bone density, immune system failure, rickets, and osteoporosis. Without enough vitamin D, our body isn't able to effectively do it’s jobs such as helping to maintain bone density, and deliver signals that run our immune system at top notch.
If you're concerned your levels are low, use our vitamin D test kit to better understand your vitamin D levels.
Curious if your lifestyle and dietary habits set you up for success with vitamin D levels? Take our vitamin D deficiency quiz to learn more!
How to Raise Your Vitamin D Levels
Raising your vitamin D levels can be an easy process if you know where to look for the nutrients. The three easiest ways to boost your vitamin D are by eating foods high in or fortified with vitamin D (such as fatty fish, cheese, egg yolks, or fortified foods like cereals, orange juice, yogurt, non-dairy milks), spending more time getting quality sunlight, or incorporating vitamin D supplements into your diet.
How Long It May Take to Recover From a Vitamin D Deficiency
The time it could take to correct a vitamin D deficiency varies based on the kinds of foods you’re eating, your activities, and your body’s ability to process nutrients. These can all play a role in your vitamin D levels. That being said, the process of improving vitamin D levels typically takes a few months.
It should be noted that even if you're looking to boost your vitamin D levels quickly and efficiently, this does not mean that “more is better”. You should not be taking more than the tolerable upper intake level (UL) of vitamin D. Negative effects, such as hypercalcemia and nausea can accompany excessive vitamin D intake.
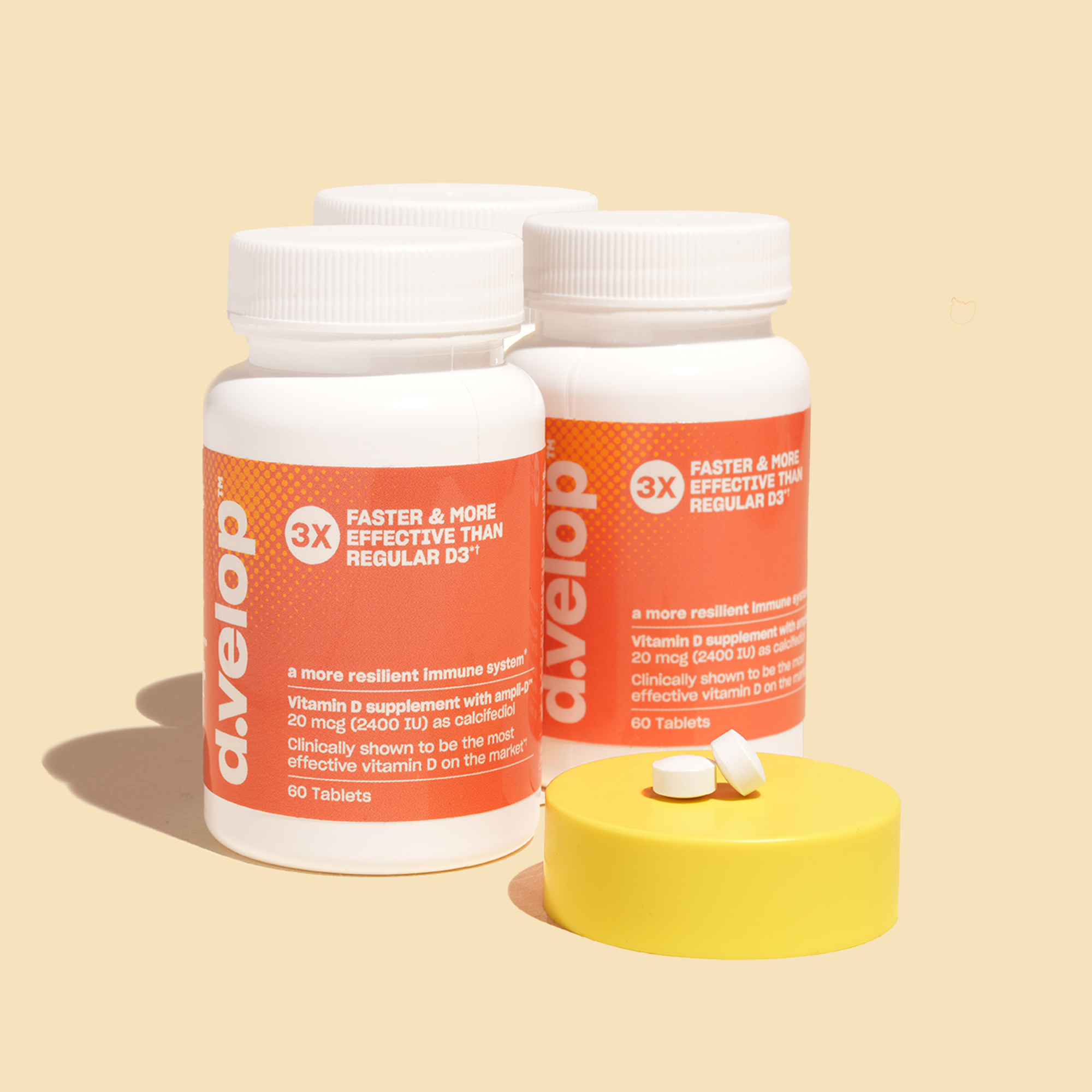
Depending on the supplements you choose to incorporate into your diet, your vitamin D levels may rise more quickly. For example, d.velop™ vitamin D supplements work 3x faster and are 3x more effective at increasing your vitamin D levels than traditional vitamin D supplements.*†
If you or your child are ready to start improving a vitamin D deficiency, check out our supplements and make a change to start improving your vitamin D levels!†
Aranow C. Vitamin D and the immune system. J Investig Med. 2011;59(6):881-886.
Sizar et al. 2021. Vitamin D Deficiency. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing.